DNA primase forms an RNA primer, and DNA polymerase extends the DNA strand from the RNA primer. DNA synthesis occurs only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. On the leading strand, DNA synthesis occurs continuously. On the lagging strand, DNA synthesis restarts many times as the helix unwinds, resulting in many short fragments called “Okazaki
Visualizing the Relationship Between Cancer and Lifespan
DNA replication is the process in which DNA is copied. It occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle. DNA must be copied so that, after cell division occurs, each daughter cell will have a complete set of chromosomes. DNA replication begins when an enzyme breaks the bonds between complementary bases in the molecule.
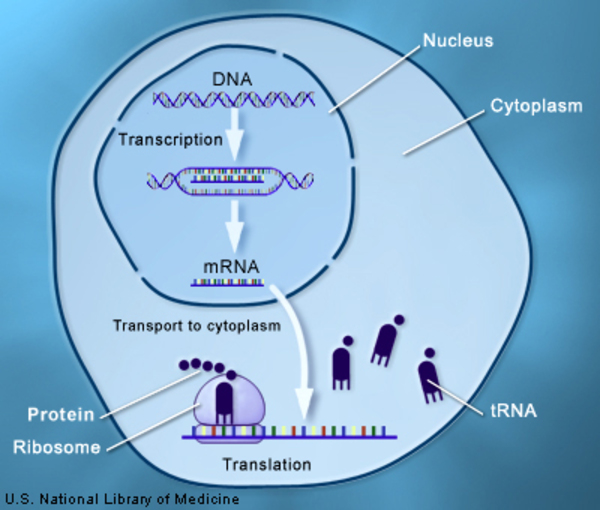
Source Image: medlineplus.gov
Download Image
The match between DNA structure and the activities of these enzymes is so effective and well-refined that DNA has become, over evolutionary time, the universal information-storage molecule for all forms of life. Nature has yet to find a better solution than DNA for storing, expressing, and passing along instructions for making proteins.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Primer Designing – Demonstration step by step – Sharebiology Jan 15, 2023DNA must be synthesized to study genes, the sequence of genomes, and many other studies. This occurs in two fashions, by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and chemical synthesis. PCR is covered in Section 28.8. Here we will focus on chemical synthesis of short DNA segments, which which are called oligonucleotides.
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
In The Figure Which Number Represents Dna Synthesis
Jan 15, 2023DNA must be synthesized to study genes, the sequence of genomes, and many other studies. This occurs in two fashions, by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and chemical synthesis. PCR is covered in Section 28.8. Here we will focus on chemical synthesis of short DNA segments, which which are called oligonucleotides. Because this sequence primes the DNA synthesis, it is appropriately called the primer. DNA polymerase can now extend this RNA primer, adding nucleotides one-by-one that are complementary to the template strand. Figure 6: First Components of DNA Replication. As DNA replication begins, DNA Helicase, a large enzyme, separates the two strands of
Electronics | Free Full-Text | Advancements and Challenges in Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review of Models, Libraries, Applications, and Algorithms
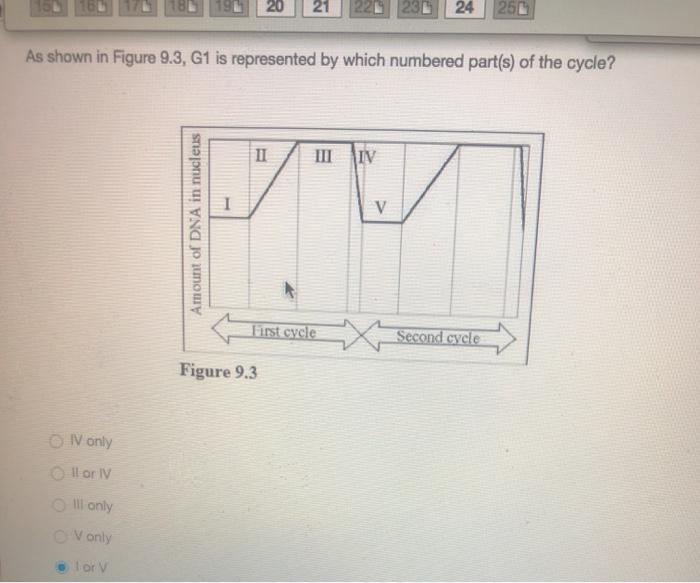
In the figure, which number represents DNA synthesis? A) 1 B) 11 C) 111 D) IV Use the following figure to answer the question. Based on your knowledge of the polarity of surrounding water molecules, the solute molecule depicted in the middle is most likely A) positively charged B) nonpolar C) negatively charged. Sure! Solved Questions 1-5 are based on the figure below. 1. In | Chegg.com

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Craft Archives | Katie Treggiden In the figure, which number represents DNA synthesis? A) 1 B) 11 C) 111 D) IV Use the following figure to answer the question. Based on your knowledge of the polarity of surrounding water molecules, the solute molecule depicted in the middle is most likely A) positively charged B) nonpolar C) negatively charged. Sure!

Source Image: katietreggiden.com
Download Image
Visualizing the Relationship Between Cancer and Lifespan DNA primase forms an RNA primer, and DNA polymerase extends the DNA strand from the RNA primer. DNA synthesis occurs only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. On the leading strand, DNA synthesis occurs continuously. On the lagging strand, DNA synthesis restarts many times as the helix unwinds, resulting in many short fragments called “Okazaki
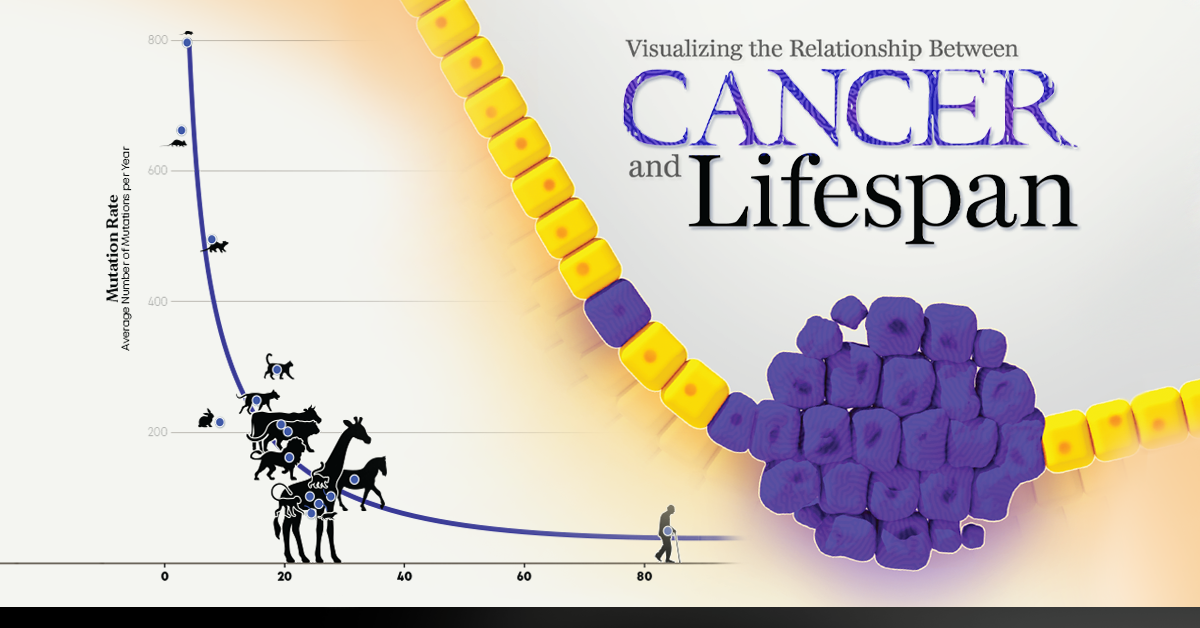
Source Image: visualcapitalist.com
Download Image
Primer Designing – Demonstration step by step – Sharebiology The match between DNA structure and the activities of these enzymes is so effective and well-refined that DNA has become, over evolutionary time, the universal information-storage molecule for all forms of life. Nature has yet to find a better solution than DNA for storing, expressing, and passing along instructions for making proteins.
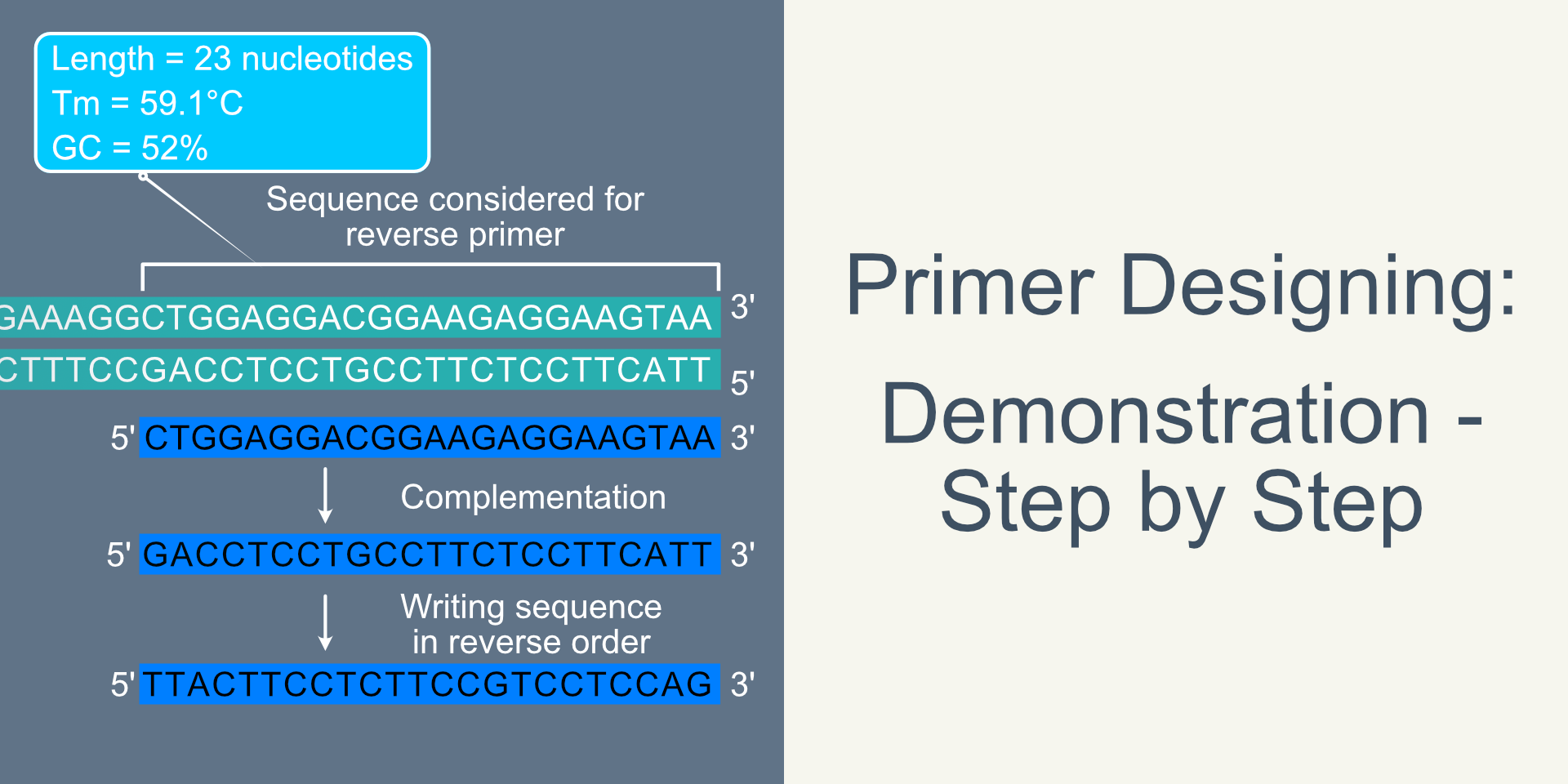
Source Image: sharebiology.com
Download Image
57 Sanger Sequencing Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors | Shutterstock The replication complex is the group of proteins that help synthesize the new DNA strands. A replication unit is any chunk of DNA that is capable of being replicated — e.g. a plasmid with an origin of replication (ORI) is a replication unit. Alternatively, this can also mean a region of DNA that is replicated together.

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Oncotarget | Predictive molecular biomarkers | EurekAlert! Jan 15, 2023DNA must be synthesized to study genes, the sequence of genomes, and many other studies. This occurs in two fashions, by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and chemical synthesis. PCR is covered in Section 28.8. Here we will focus on chemical synthesis of short DNA segments, which which are called oligonucleotides.
Source Image: eurekalert.org
Download Image
beta cells – NIH Director’s Blog Because this sequence primes the DNA synthesis, it is appropriately called the primer. DNA polymerase can now extend this RNA primer, adding nucleotides one-by-one that are complementary to the template strand. Figure 6: First Components of DNA Replication. As DNA replication begins, DNA Helicase, a large enzyme, separates the two strands of
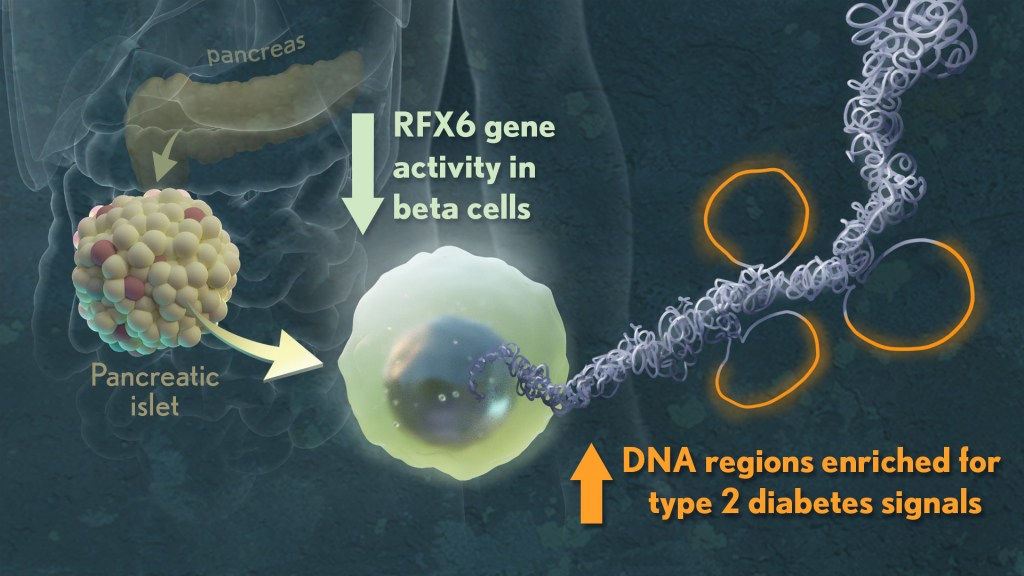
Source Image: directorsblog.nih.gov
Download Image
Craft Archives | Katie Treggiden
beta cells – NIH Director’s Blog DNA replication is the process in which DNA is copied. It occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle. DNA must be copied so that, after cell division occurs, each daughter cell will have a complete set of chromosomes. DNA replication begins when an enzyme breaks the bonds between complementary bases in the molecule.
Primer Designing – Demonstration step by step – Sharebiology Oncotarget | Predictive molecular biomarkers | EurekAlert! The replication complex is the group of proteins that help synthesize the new DNA strands. A replication unit is any chunk of DNA that is capable of being replicated — e.g. a plasmid with an origin of replication (ORI) is a replication unit. Alternatively, this can also mean a region of DNA that is replicated together.